Cross-contamination is one of the most common causes of food poisoning. It occurs when raw food contacts with cooked or ready-to-eat food, equipment or surfaces. It can also happen if the same equipment is used for raw and cooked or ready-to-eat food. Hands can also spread germs if not properly washed after handling raw food. To prevent cross-contamination, adequately separating raw and cooked or ready-to-eat food is important.
-
Before cooking food, food preparation surfaces must be cleaned with hot water and cleaning agents to ensure there is no contamination.
-
Use separate food preparation areas for handling of raw, cooked, ready-to-eat and high-risk foods (e.g. oysters for raw consumption and sashimi). No unauthorised switch of area use is allowed. If raw, cooked and ready-to-eat foods need to be handled in the same preparation area, disinfect the area thoroughly between uses.
-
Food and drinks should not be prepared on the floor, near the toilet or drains, or in any areas outside the kitchen or stalls.

-
Washing raw meat and poultry may cause cross-contamination too because bacteria in splashes can spread up to 80 cm from the sink, contaminating adjacent surfaces, utensils or foods. If the washing step is necessary, thorough cleaning of the kitchen sink and surrounding areas is required to prevent cross-contamination.
-
When preparing pooled eggs, be careful not to spill them on other foods or surfaces. After pooling eggs, clean the utensils around.
-
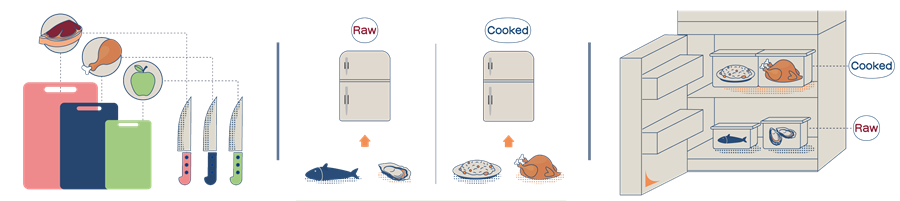
Handle raw foods (e.g. raw meat) and cooked foods (e.g. poached chicken) or ready-to-eat foods (e.g. fruits) by using designated utensils, including cutting boards, knives and wiping cloths. Colour coding can be applied to utensils for different foods.
-
Ideally, use two separate refrigerators for storing raw foods and cooked or ready-to-eat foods.
-
If raw foods and cooked or ready-to-eat foods must be stored in the same refrigerator, store foods in containers with lids. Cooked or ready-to-eat foods should be placed on the upper shelf of the refrigerator, and raw foods in the lower part. This prevents juices of raw foods from dripping onto cooked or ready-to-eat foods.
-
Powdery ingredients, spices and other dried foods should be stored in dry areas and should not come into contact with wet utensils or wooden spoons to avoid introduction of and subsequent contamination by mould. Use a fresh spoon for each tasting. Used spoons should not come into contact with food again.
-
Detergents and other chemicals should be kept away from food preparation areas. Click here for details about chemicals handling.
 |
Proper hand and personal hygiene is essential for minimising cross-contamination of food. So please remember:
Revisit the "Personal hygiene" section to review the key points of personal hygiene. |